Smart personal audio vendors capitalize on the impending hearing health crisis
With a global increase in the number of individuals experiencing hearing loss, smart personal audio vendors are venturing into the over-the-counter hearing aid market. This strategic move aims to diversify their strategies and revenue streams, enabling them to compete more effectively with smartphone ecosystem vendors in the highly competitive smart personal audio market.
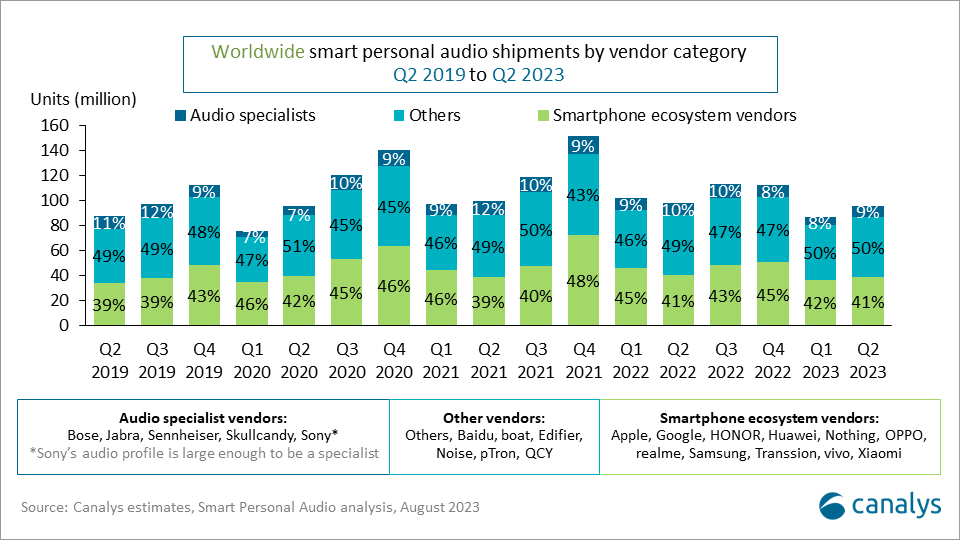
Differentiation in the smart personal audio market is challenging due to the simplistic nature of personal audio devices, leading to standardized products where consumers increasingly prioritize value, convenience, price and brand image. As the smart personal audio market developed, smartphone and IoT ecosystem vendors outperformed specialist audio counterparts, offering lower-priced products driven by scale economies. The continuing preference of smartphone ecosystem vendors is further fuelled by convenient purchasing, bundling and ecosystem interoperability.
In recent years, "audio specialist" vendors have entered the over-the-counter (OTC) hearing aid market, following FDA initiatives in 2017 to open the market (available since 2022). The OTC hearing aid market was valued at US$1.06 billion in 2022, with significant growth potential due to:
- Affordability: OTC devices reduce costs by up to US$3,000 per pair, eliminating the need for exams, fittings and prescriptions. Prescription hearing aids, typically not covered by medical insurance plans, make OTC options more accessible. They often include extra features like Bluetooth connectivity to devices and customizable apps.
- Suitability: noise-induced hearing loss, labeled a growing public health crisis by the Hearing Loss Association, is propelling expansion in the recently established market. Delicate ears, not designed for prolonged exposure to loud noises, can suffer damage to in-ear hair cells and the auditory nerve. Globally, over 1.5 billion people are affected by hearing loss, a number projected to reach 2.5 billion by 2050. The widespread use of headphones, particularly in-ear devices, exacerbates the issue. With more children and adults extending headphone usage, cases of hearing damage are expected to rise. A concerning CDC estimate reveals that 12.5% of Americans aged six to 19 experience hearing loss due to loud music.
- Scope: significant scope for further AI integration that would provide a more personalized and extensive experience. For example, it could listen for voices that one hears most often and prioritize them in a crowded setting or provide automatic enhancement adjustments depending on the time of day.
Notable smart personal audio vendors who produce OTC hearing aids include:
- Sennheiser (with Sonova aid)
- Jabra (with GN Group aid)
- Sony (in partnership with W.S. Audiology)
- Zepp Health
Rumors swirl of JLab developing two of their own OTC hearing aids.
Specialized audio vendors facing continuous competition need alternative strategies. Embracing OTC hearing aids provides a distinct and revenue-diversifying approach, offering substantial long-term growth prospects. A top-performing OTC hearing aid can set vendors apart, expanding their device ecosystem, enhancing revenues, attracting new consumers and fostering brand loyalty by showcasing their technical expertise. Audio specialists can target the growing number of those with mild to moderate impairment.
Ecosystem vendors have taken a different approach to combatting this hearing health issue. Instead of developing OTC hearing aids, leading vendors like Apple and Samsung have recently integrated hearing health features into their flagship devices.
Samsung:
- Samsung introduced the "ambient sound" mode. The feature works by utilizing the microphones in the headphones to amplify surrounding sounds, allowing users to fine-tune ambient sound across five levels of amplification and various settings, effectively providing hearing aid capabilities.
Apple:
- Conversation Boost focuses on enhancing conversation sounds by using the microphone to capture the dialogue in front of the user.
- Live Listen utilizes the microphones on iPhones and AirPods in the same fashion as Samsung’s "ambient sound" mode.
Integrating these features into flagship TWS devices targets consumers with low to mild hearing damage. With a rising prevalence of low-level hearing issues, these consumers are likely to prioritize TWS devices over OTC and prescription aids, finding sufficient improvement from the enhancement features. This will become an important factor in the purchasing decisions of individuals with mild hearing impairments. As the prevalence of hearing damage increases, the effectiveness of these features will be a crucial differentiation, essential for long-term success in the premium TWS market.
These devices would substitute OTC and medical hearing aids for moderate to severe hearing damage. Short-term purchasing decisions are limited by current awareness, the prevalence of hearing health issues and early product capabilities. It is unlikely that these enhancements will substantially boost vendor revenue, given the substantial costs of investment, development and testing required to compete with OTC devices (which is likely to be unachievable, regardless). The considerable product markups (often surpassing 60%) and growth potential in the OTC market seem more appealing.
Ecosystem vendors entering the OTC space currently appear unlikely due to their focus on TWS enhancement integration. Additionally, they would trail competitors with established devices and expertise. Jabra and Sennheiser receive support from sister-brand hearing aid companies and Sony partners with the hearing aid giant W.S. Audiology. If revenues justify, smartphone ecosystem vendors aiming for an OTC share might need to acquire or heavily invest in a partnership with a hearing aid vendor, not established in the current OTC market.
While specialists may not capture significant shipment share from ecosystem vendors, the substantial revenue from OTC hearing aid growth can fund personal audio device development and enable aggressive pricing. This yields a renewed competitive edge, alongside discussed brand benefits and the potential for hearing enhancement that AI brings after being integrated into their personal audio devices.
The OTC hearing aid market is positioned to provide audio specialists the brand, feature and financial means to compete successfully in the challenging smart personal audio market over the long term.
Share this article
CATEGORY
- All
- Canalys Forums
- Canalys Forums,Channels
- Canalys Forums,Channels,Partner Program
- Canalys Forums,Channels,Sustainability
- Canalys Forums,Sustainability
- Enterprise
- Market
- Market,Canalys Forums,Channels
- Market,Canalys Forums,Channels,Cloud
- Market,Canalys Forums,Channels,Sustainability
- Market,Channels,PC
- Market,PC
- Market,Smartphone
- Market,Technology,AR/XR/VR
- Market,Technology,Automotive
- Market,Technology,Canalys Forums,Channels
- Market,Technology,Canalys Forums,Channels,Cloud
- Market,Technology,Channels
- Market,Technology,Channels,Cloud,Partner Program
- Market,Technology,Smart Personal Audio
- Market,Technology,Smart Speaker
- Market,Technology,Smartphone
- Smart Personal Audio
- Smartphone
- Technology
- Technology,Canalys Forums,Channels,Security
- Technology,Channels
- Technology,Channels,Cloud,Partner Program
- Technology,Channels,Partner Program
- Technology,Unified Communications
- Technology,Wearable Band

